In the ever-evolving landscape of telecommunication infrastructure, geographic information system (GIS) technology emerges as a powerful tool in the management and protection of outside plant infrastructure (OSP). This blog article delves into the transformative role of GIS in OSP management, exploring how mapping and monitoring technologies contribute to efficient and resilient telecommunication networks.
Understanding GIS In OSP Management
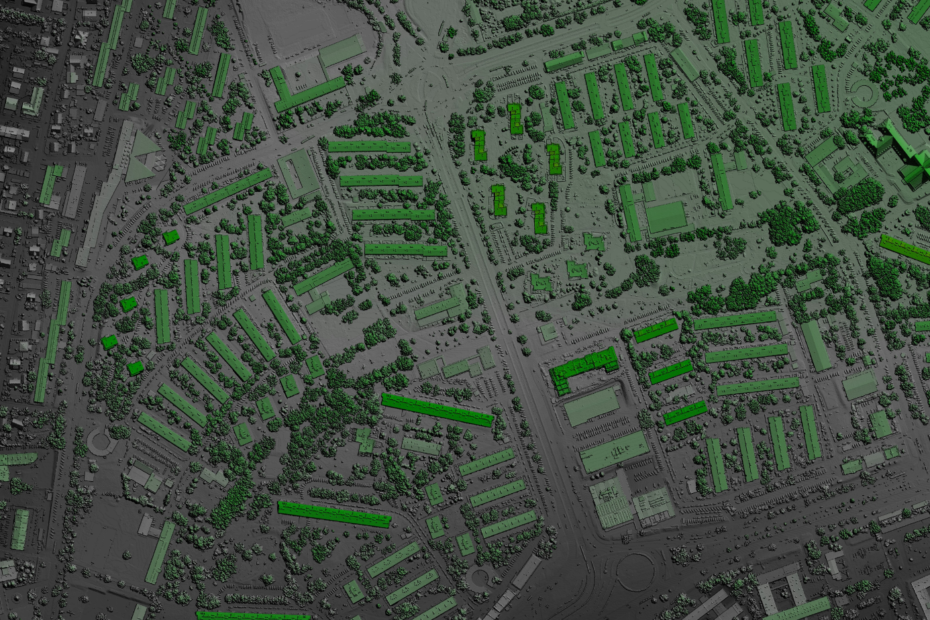
Geographic information system (GIS) is a technology that captures, analyzes, and interprets spatial and geographic data. In the context of OSP management, GIS plays a pivotal role in mapping the physical location of network components, providing real-time insights, and facilitating informed decision-making processes.
Mapping The OSP Landscape
1. Precise Infrastructure Mapping: Firstly, GIS allows for the precise mapping of OSP components, including fiber optic cables, distribution points, and other critical elements. This accurate representation aids in efficient network planning, maintenance, and expansion.
2. Spatial Data Visualization: Secondly, visualization of OSP data in a spatial context enables telecom operators and engineers to understand the geographical distribution of network elements. This aids in identifying potential vulnerabilities, optimizing resource allocation, and planning for future infrastructure development.
Real-Time Monitoring & Analysis
1. Dynamic Network Monitoring: GIS technology enables real-time monitoring of OSP components. Through the integration of sensors and monitoring devices, telecom operators can receive immediate alerts for any anomalies or disruptions in the network, facilitating rapid responses to potential issues.
2. Performance Analytics: GIS provides tools for performance analytics, allowing telecom operators to assess the efficiency and reliability of OSP components. This data-driven approach enables proactive maintenance, reducing downtime and enhancing the overall resilience of the telecommunication network.
Strategies For GIS-Enhanced OSP Management
1. Integration With IoT Devices: Firstly, incorporating GIS with Internet of Things (IoT) devices for comprehensive data collection. This synergy enhances the granularity of OSP data, providing a more detailed and accurate representation of the network’s real-time status.
2. Predictive Analysis: Secondly, utilizing GIS for predictive analysis to forecast potential challenges in OSP components. By analyzing historical data and environmental factors, telecom operators can anticipate issues and implement preemptive measures to safeguard the network.
Collaborative GIS Applications
1. Industry Collaboration: Collaborating with GIS service providers, telecommunication companies, and regulatory bodies to create standardized GIS applications. This collaborative effort ensures interoperability and the development of best practices for OSP management across the industry.
2. Public Participation: Engaging with local communities and authorities through GIS platforms to incorporate their insights into OSP planning. Public participation ensures that OSP projects align with community needs and minimizes potential conflicts during infrastructure development.
Challenges & Future Developments
1. Data Security & Privacy: Addressing concerns related to data security and privacy when utilizing GIS technology for OSP management. Ensuring robust security measures to protect sensitive information and complying with privacy regulations.
2. Advancements In GIS Technology: Embracing future advancements in GIS technology, such as augmented reality integration and machine learning algorithms, to further enhance the accuracy and efficiency of OSP mapping and monitoring.
Ultimately, GIS technology emerges as a cornerstone in the management and protection of OSP, mapping the future of telecommunication infrastructure. As GIS continues to evolve, its integration into OSP management processes will be pivotal in navigating the dynamic landscape of telecommunication infrastructure.
Learn More
To find out about how Phoenix Loss Control can help when outside plant infrastructure damages occur, please click here.
For additional reading on integrating GIS (and other new technology trends and standards) in OSP engineering, check out this article.